What is Septoria or Septoriasis in cultivation?
List of contents
If you have ever cultivated, even if you have never done it before, surely you know that fungi are one of the main enemies of crops throughout the world. These microscopic organisms can spread rapidly in plants, causing a variety of diseases that can significantly reduce crop production and quality. Fungal pests can affect a wide range of plants, from cereals and vegetables to fruits, forest crops, and of course cannabis, causing damage with a significant economic impact for farmers and the food industry.
Septoria is a fungal disease that affects a wide variety of plants, including crops such as tomatoes, potatoes, and wheat. This disease is caused by fungi of the genus Septoria, which spread through spores and are characterized by the appearance of small, dark spots on the leaves of the plant, which eventually spread and become necrotic. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and preventive and control measures of this disease to help you protect your crop.

What is Septoria?
Septoria is a disease caused by various fungi of the genus Septoria, including Septoria lycopersici, which causes leaf spots on tomatoes, and Septoria tritici, which causes yellow spot disease on wheat. These fungi can survive on infected plant debris and in the soil, and spread through spores that are dispersed through the air, water, or insects that act as disease vectors.
Septoria infection begins when spores of the fungus come into contact with the leaf surface of a plant. Once the spores germinate, the fungus begins to grow and develops on the leaf, forming its characteristic spots. As the infection progresses, the spots may cover large areas of the leaf, which may begin to yellow and drop prematurely from the plant.
How does Septoria reproduce?
Septoria reproduces by means of spores produced by the fungus Septoria spp. These spores are small and can be carried by wind and rain from one infected plant to another. They can also be carried by insects and other organisms that feed on infected leaves.

From the moment Septoria spores are deposited on a leaf, they can germinate and penetrate the plant tissue. Once inside the leaf, the fungus develops and reproduces, producing more spores that disperse to other parts of the plant and to nearby plants.
Septoria can survive in infected plant debris and in soil for several years, allowing the fungus to spread through multiple growing seasons. The spores can also be carried on farm equipment and on the clothing and shoes of people who work in the crops. It will therefore be especially important to take preventive measures to prevent the spread of the disease and reduce its impact.
What type of climate favors Septoria?
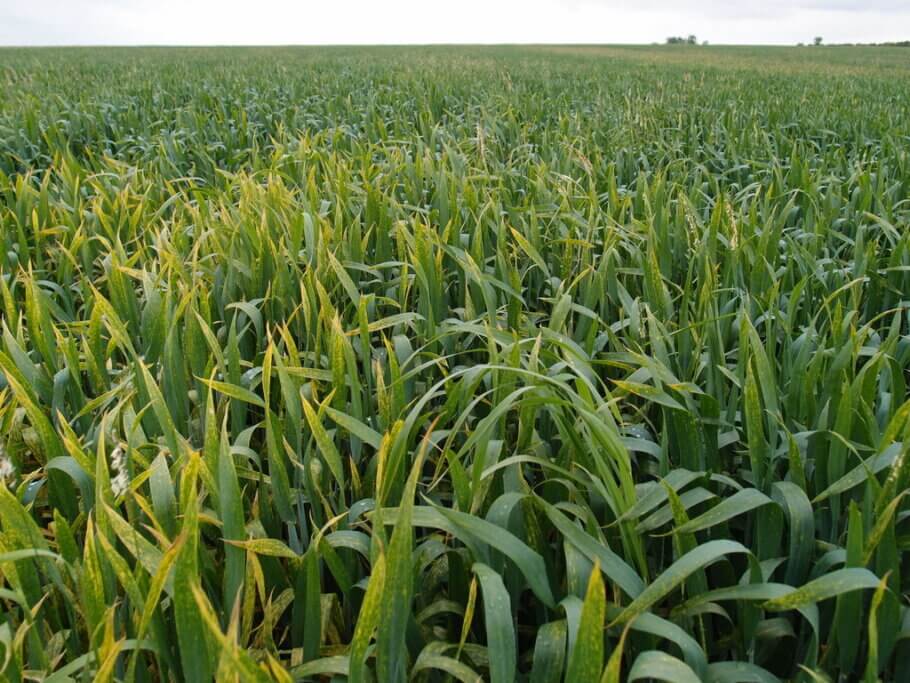
Septoria can be favored by a humid and warm climate, which can occur in a good part of the world. Spores of the fungus can spread through the air and are deposited on plant leaves, where they germinate and penetrate the leaf tissue. The infection spreads more rapidly in conditions of high humidity and mild temperatures, around 20-25°C, which are ideal for the growth of the fungus.
Therefore, this disease may be more prevalent in areas with frequent rainfall and high environmental humidity. Prolonged wetness on the leaves provides a favorable environment for the growth and transmission of the fungus, which can lead to the rapid spread of the infection.
On the other hand, dry and hot conditions can reduce the incidence of the disease, since the lack of humidity limits the growth and spread of the fungus. However, extremely hot and dry weather can also cause stress in plants, making them more susceptible to both this disease and other problems. It will be necessary, then, correct hydration of the plants under these conditions.

Septoria symptoms and damage
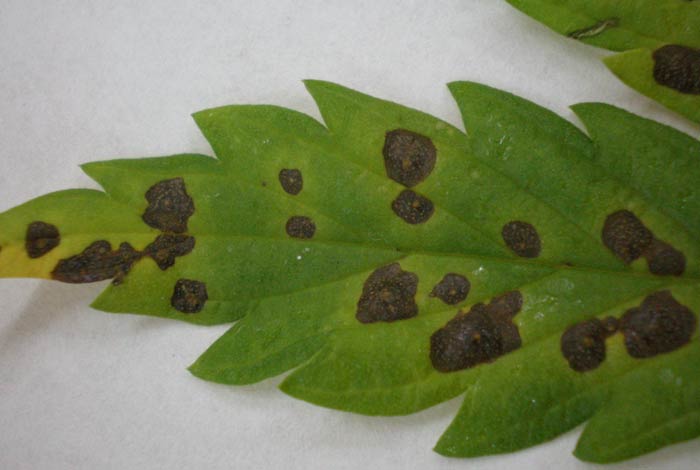
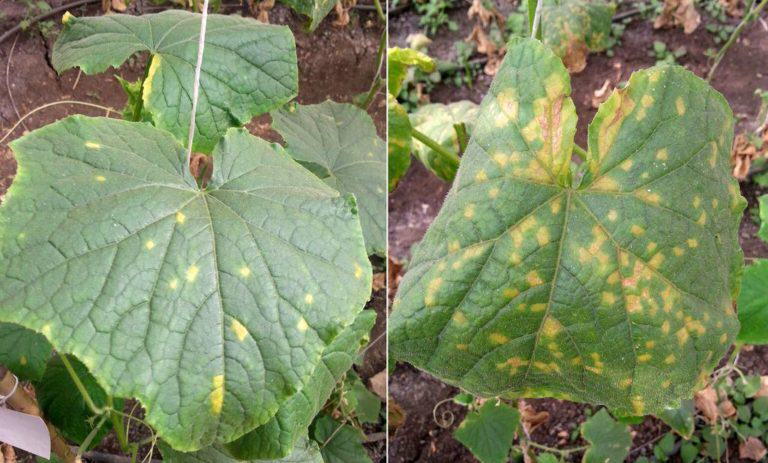
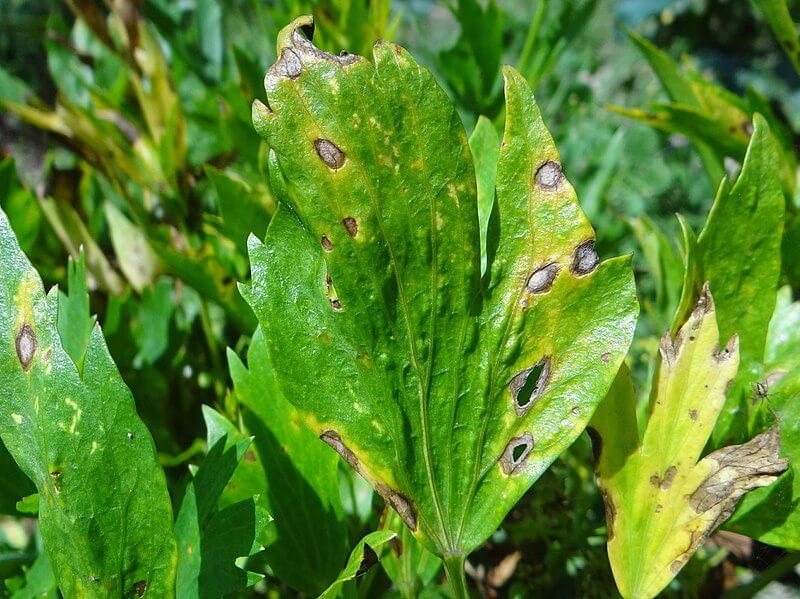
Symptoms of Septoria disease can vary depending on the species of fungus and the type of plant infected. However, in general, the symptoms include the appearance of small, dark spots on the leaves of the plant, which can be up to 1 cm in diameter. These spots are usually circular or oval in shape, usually surrounded by a yellow or light brown border.
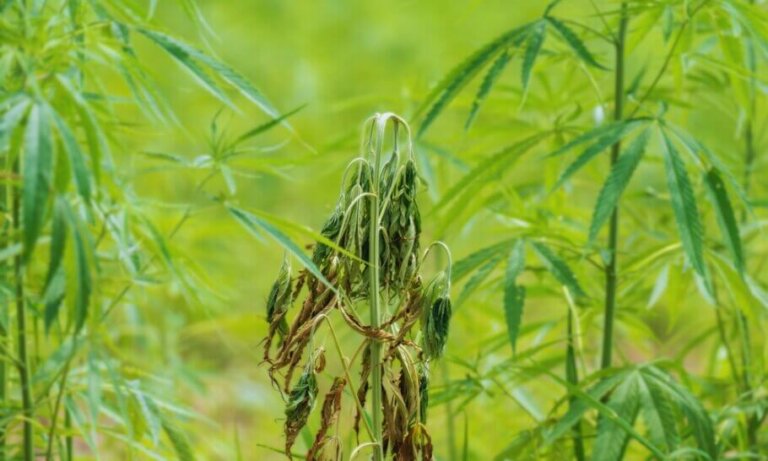
As the infection progresses, the spots become larger and may coalesce, covering large areas of the leaf. Infected leaves may begin to turn yellow and drop prematurely from the plant, which can weaken the plant and reduce fruit or grain production.
In the case of tomato crops, for example, it can cause a significant decrease in the production and quality of the fruits. Infected plants can produce smaller, less flavorful fruit, and the disease can spread to other parts of the plant, such as stems and branches.
In the case of wheat and other cereals, the yellow spot disease caused by Septoria tritici can cause a significant decrease in grain yield and wheat quality. The disease can reduce the weight of the grains and the amount of protein, which can have a negative impact on the quality of the flour.

Prevention and treatment of Septoria
Prevention of Septoria disease is essential to protect crops from fungal infections. One of the best ways to prevent the disease is through proper growing practices, such as crop rotation, removing infected plant debris, and using healthy, hardy seeds.
Other practices that can help prevent the disease include reducing stress on the plant, such as proper watering and balanced fertilization. Additionally, it is important to maintain a clean, weed-free environment around the plants to reduce moisture and spore spread.
How to water marijuana plants in soil
In this post we present a simple and useful way to properly water your marijuana plants. There are many mistakes made with irrigation, but with four simple steps you can rest easy and get an excellent harvest. From lack of watering to excess, today we will tell you everything you need to know to water your plants correctly, thus avoiding many worries.
If a Septoria infection is detected, it is important to take immediate control measures. Treatment of this disease may include the use of fungicides and pruning infected parts of the plant. Fungicides are usually applied to infected leaves to kill the fungus and prevent the spread of the disease to other parts of the plant. However, it is important to use fungicides responsibly and follow the manufacturer's recommendations to prevent fungal resistance to fungicides.
Another effective control method is the use of plant varieties resistant to the disease. By choosing Septoria-resistant plant varieties, farmers can reduce the need for fungicides and prevent future infections, while also improving crop yields.
Happy harvest!