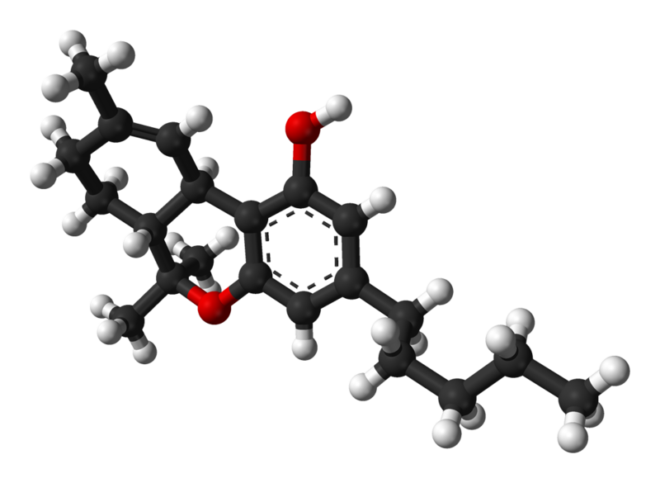
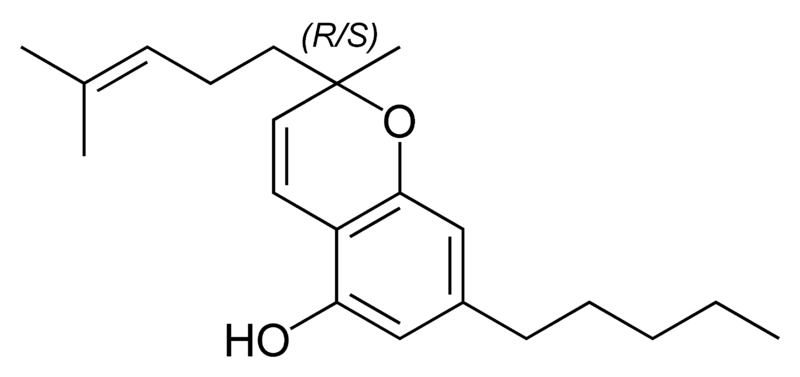
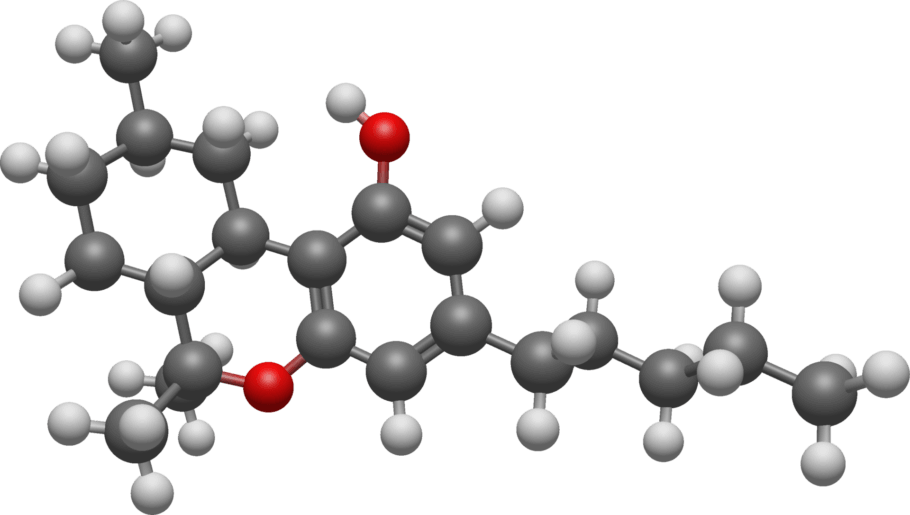
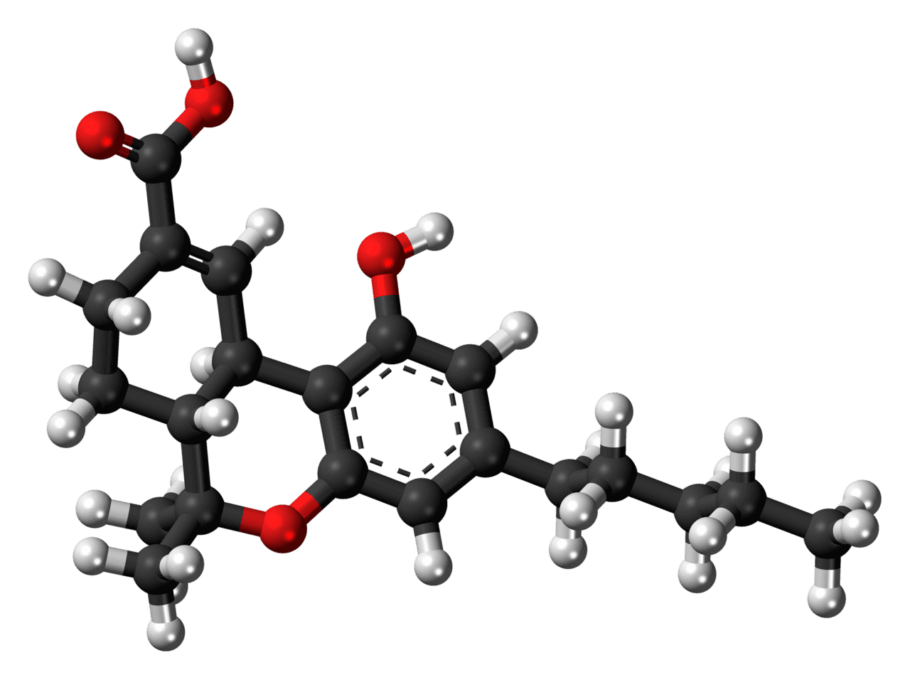
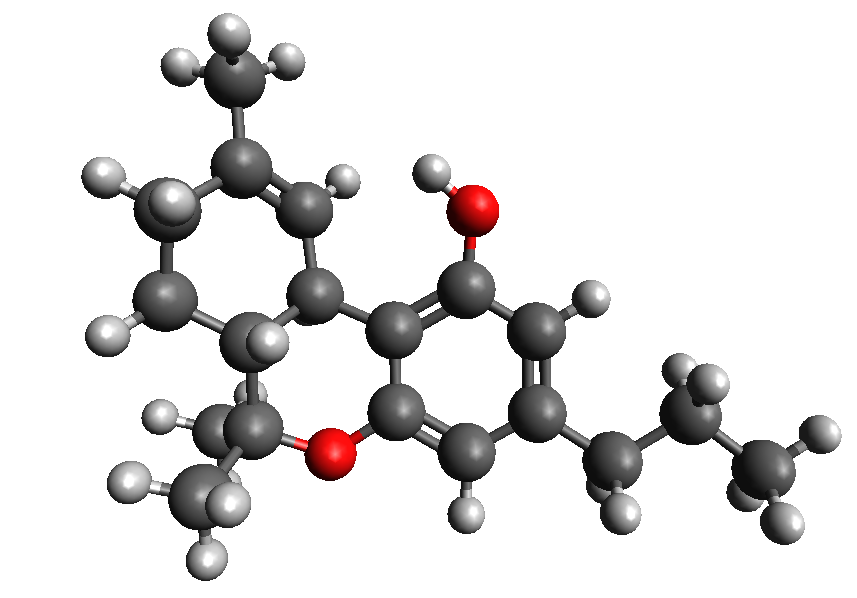
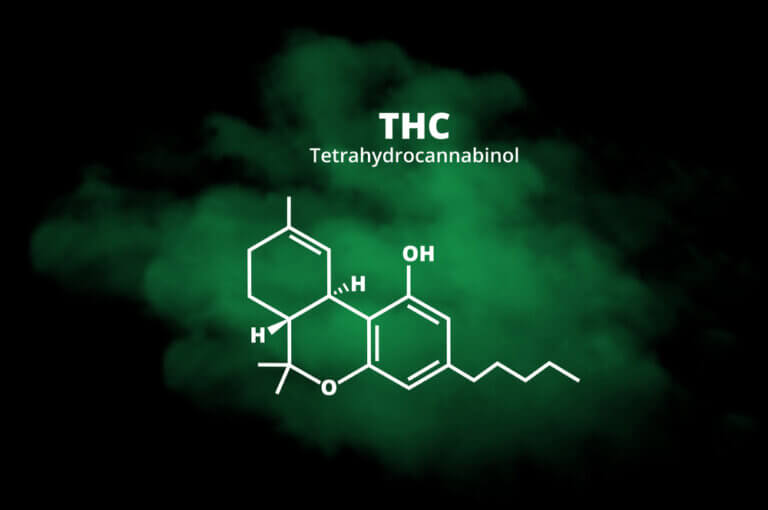
THC-JD or Tetrahydrocannabioctyl

Scientific research on the different cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant does not stop, and new compounds are being discovered and studied continuously, each with its characteristics and potential benefits. One of these emerging compounds is THC-JD, also known as Tetrahydrocannabioctyl. This relatively unknown cannabinoid is beginning to attract the attention of researchers and plant enthusiasts for its potential unique effects and medicinal applications.
THC-JD, unlike its more famous relatives such as THC and CBD, is found in much lower concentrations in the cannabis plant. However, its chemical properties and therapeutic potential have sparked great interest in the scientific community. Early studies suggest that THC-JD could have more potent and specific effects, offering new opportunities for the treatment of various medical conditions.
This article will explore in depth what THC-JD is, how it differs from other cannabinoids, its potential benefits and effects, and what its discovery could mean for the future of medicinal and recreational cannabis. As we advance our understanding of cannabinoids, THC-JD could play a key role in developing new treatments and expanding knowledge about cannabis use.