Marijuana terpenes and their effects
List of contents
The genetic diversity of marijuana
Each marijuana plant coming from seed has a cannabinoid profile, unique taste and olfactory molecules, which are not found in the same way in any other plant. This combination of possibilities creates countless variations in the flavours and effects of marijuana, and are highly valued by growers, who can discover new emotions when growing different strains, or may start breeding projects in order to select the plant that best suits their needs or priorities.
The wide range of flavours and effects offered by the different strains of marijuana also helps you to avoid developing tolerance to its effects: when you have a single variety, the user and his or her body will develop a resistance - tolerance - to the properties of the plant consumed.
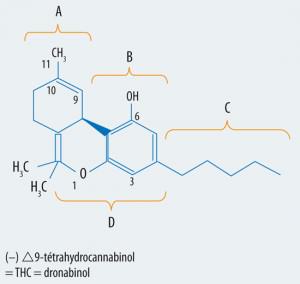
For a long time we have known that THC and THC-V are primarily responsible for the psychoactive effects of marijuana. Other cannabinoids (CBD, CBN, CBC, CBG ...) have little effect of this type. In this case, how can we explain the variations of the effects that can be observed from one plant to another?
Terpenes, aromatic molecules in plants

Let?s take a look at one of the components that make up the smell of marijuana. Between 10% and 30% is composed of terpenes, which are aromatic molecules produced in the resin of the plant. Most of the scents and smells that we associate with plants are the result of terpenes (and flavonoids). Conversely, cannabinoids do not have any aroma or smell.
Because plants can not move, can not escape predators or flee when neighbouring plants overwhelm their territory, they have developed a very efficient defence strategy, primarily based on chemical warfare.
Terpenes ensure several functions: for example, some of them keep predators away, others kill them, others slow their maturation, and others affect their metabolism somehow. Plants use other aromatic molecules to attract pollinating insects -thus ensuring reproduction - or to attract predators of their enemies. Apart from these, there are also other terpenes that can develop because of stress of the plant(excess heat, etc).
Terpenes are a major component of the so-called essential oils from plants. Aromatherapy uses the medicinal properties of these terpenes to regulate mood, sleep problems, acuity and overall health. For example, the essential oil from lavender is calming and relaxing, while rosemary increases concentration and produces a feeling of well being.
It is possible to make essential cannabis oil through steam extraction. It is used in perfumes, cosmetics, soaps, candles, and also as a flavouring agent in cooking, such as candies and beverages (beer flavoured with marijuana ...)
Once marijuana has been harvested it contains about 1% essential oil, composed mostly of very volatile monoterpenes (80-90%), that evaporate very quickly. Once the weed is completely dry, the amount of essential oil is only 0.1%, and about 50% of this is made of sesquiterpenes, which are far less volatile.
What are marijuana terpenes?
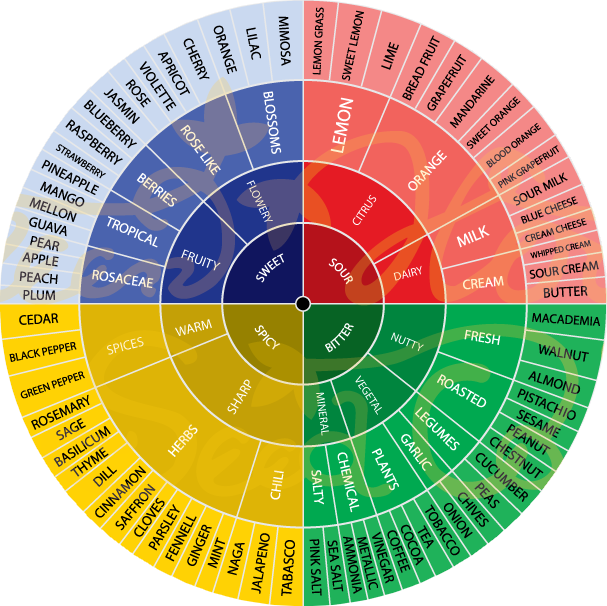
More than 100 different terpenes have been detected in marijuana, and there are many more if we consider the different variations of each one. For example, the typical smell of citrus fruits comes from terpenes called limonenes, but these can vary in concentration. The limonenes of a lemon are identical to the limonenes of an orange, but each variety is defined by a different smell, resulting from tiny differences in the proportions or the form of the limonenes that it contains.
Here we list the main terpenes found in Cannabis Sativa and its effects on our health. You will see that percentages can vary widely from one variety to another,:
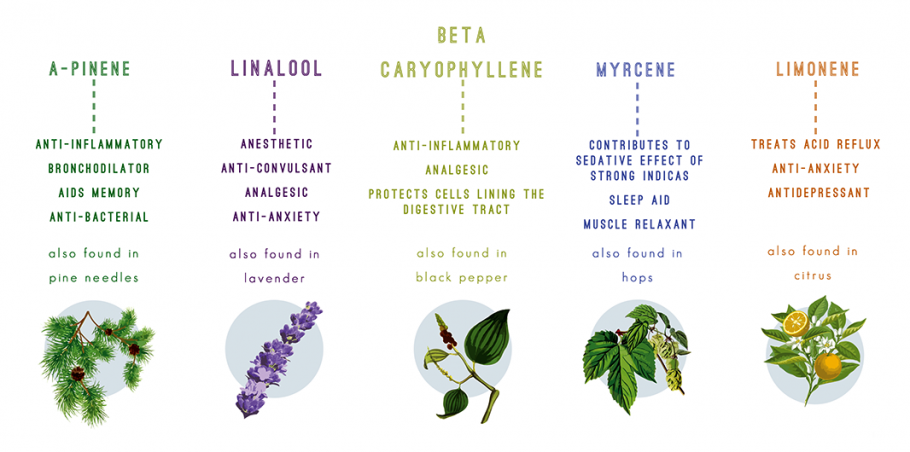
Myrcene

Myrcene is the most common terpene in marijuana strains (up to 60% of the essential oils of certain varieties) however, it is not found in hemp textiles. It is also found in large quantities in hops or in the West Indian wood (Saint Thomas Bay). Its smell is very similar to cloves (girofle). Myrcene is a potent analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antibiotic. It blocks the action of cytochrome, aflatoxin B, and other pro-mutagenic carcinogens. It also has a relaxing, calming, anti spasmodic and sedative effect. Acting in synergy with THC, myrcene increases its psychoactive potential.
Limonene
Limonene is often the second, third or fourth terpene found in cannabis resin. This family of terpenes produces the typical smell we all recognise as citrus. Limonene has anti fungal and anti bacterial properties and is also anti

carcinogenic. It prevents the detioration of the RAS gene, one of the factors that contribute to the development of tumors. It also protects against Aspergillus and carcinogens present in smoke. Limonene quickly and easily penetrates the blood-brain barrier, which increases systolic pressure. During testing on the effects of limonene, participants experienced an increase in attention, mental focus, well-being and even sex drive. Limonene is used sometimes in spray form, to treat depression and anxiety. It also has the effect of reducing the unpleasantness of gastric acid and stimulates the immune system. Plants use limonenes to ward off predators; for example, it repells flies like any insecticide.
Caryophyllene
Caryophyllene can be found in various herbs and spices, particularly in black pepper, which contributes to the spicy flavour. It is a local anti inflammatory and analgesic, and one of the active ingredients of the clove (Giroflé). It is an

efficient remedy to relieve toothache. It also has anti fungal properties. This terpene has the particularity of selectively activate the cannabinoid 2 receptors (CB2), while it is not a cannabinoid. This discovery opens the door to many possibilities in medicinal research.
Pinene
Pinene is responsible for the familiar smell associated with pine and fir trees, and to be more precise, its resin. It is the main ingredient of the essence of turpentine. It is present also in many plants such as Sage or Rosemary. Pinene is used in medicine as an expectorant, bronchodilator, anti inflammatory and local antiseptic. It also crosses the hemato encaphalic barrier very easily, where it acts as an inhibitor of acetylcolynesterasics, preventing the destruction of molecules responsible for the transmission of information, which results in memory improvement. It

is largely due to the presence of pinenes that Rosemary and Sage have been considered to be beneficial plants during thousands of years of traditional medicine. This terpene ca, in part, counteract the effects of THC, which leads to a decrease in the acetylcholine levels. The result is that the memory fails more with pure THC than with THC mixed with pinene. Skunk strains are, for example, recognised for their high levels of pinenes. Because this produces a bronco dilator effect, the smoke of plants rich in pinene give the sensation of sucking more air, which can cause hyperventilation or sometimes cough. Pinene also improves concentration, personal satisfaction and energy, but it may be limited by the effects of the terpinol.

Terpineol
Terpineol smells of lilac, crabapple blossoms and lime blossoms. During tests on mice, their mobility was reduced to 45%. This explains the sedative effect of some marijuana strains. Terpineol is often found in strains that have a high level of pinenes, the aromas of which can hide the smell of terpineol.
Borneol

Borneol has aroma of mint and camphor. It is used in Chinese medicine against fatigue, stress, or to recover from illness. The Super Silver Haze Marijuana strain from Sensi seeds is known for its camphor aromas, and its effect is both relaxing and psychedelic. Hence, we can suppose that it contains a good amount of borneol.
Linalool

Linalool has a floral smell like lavender and spring flowers. Humans are able to smell it at very low levels, from 1 PPM in air. Linalool is currently used in the treatment of various cancers. It also has a powerful calming action, anti anxiety, and produces a sedative effect. In tests on mice it was discovered that their activity decreased by 75%. Linalool is thus partly responsible for the sedative effects of certain marijuana strains. It also has analgesic and anti-epileptic properties.
Eucalyptol
Eucalyptol (also called 1,8-cineol) is the main ingredient of eucalyptus essential oil. It has the characteristic

minty smell of this tree and is also found in small amounts in marijuana. Its effects relieve pain and improve concentration and inner balance. Plants containing eucalyptol enhance meditation and concentration.
Nerolidol
Nerolidol, with woody and fresh bark aromas, can be found in ginger, niaouli and citronella. It has anti fungal, anti leishmaniasis and anti-malarial properties. It also produces a sedative effect.
Other Terpenes
Other terpenes that can be found in marijuana resin are, for example, phellandrene, phytol, humulene, pulegone, bergamotene, farnesene, D3-carene, elemene, fenchol, aromadendrene, bisabolene, and many more...
We see then that the endless possibilities of terpene profiles are responsible for variations in taste and effects of marijuana. Some combinations of terpenes can act in synergy (the effects are added), while others are antagonists (the effects inhibit each other). Some terpenes increase the assimilation of THC, while others affect the flow of dopamine and serotonin, two of the main regulators of mood and behavior.

We know that some medical marijuana users have noticed that one plant in particular helps them more than others. When analysing these plant cannabinoids we see, however, that they have the same or very similar levels than other plants whose effects are lesser. We can see that some terpene profiles, together with suitable cannabinoid rates, are more effective for patients than other similar varieties. We notice then, through the effects of marijuana, that terpenes do have a role. Unfortunately, current chromatography techniques do not allow accurate identification of all terpenes present in marijuana.
This diversity offered by nature is impossible to reproduce for the pharmaceutical industry, which attempts to isolate the active principles in order to patent its synthetic reproduction. Pure THC causes very different effects than marijuana because it is missing all the terpenes and cannabinoids that modulate its effect.
The plant?s age, maturity, and time of harvest may also modulate the levels and amounts of terpenes. Usually, the smell becomes more intense during flowering, but it can vary depending on weather conditions, environment (fertilizers ...), or plant stress. You will notice, for example, the smell of a plant is usually stronger earlier at dawn than at dusk.
Terpenes are responsible for both the flavour and aroma of the plant. It is important to remember that a plant with little aroma will always have little flavour.
Terpenes and their interactions on the brain is a fascinating subject, which opens the way to numerous medical researches and another level of exploration and creativity for seedbanks. Through recognizing the different families of terpenes, we can predict the effects of a marijuana bud only with its smell!
Mango, myrcene and marijuana?

According to several sources, eating a good ripe mango 45 minutes before smoking marijuana increases the effect of the herb. This could be explained by the presence of Myrcene in mangos, which acts in synergy with the THC.
But according to our research, we should select a very good variety of mango, because only a few have essential oil rich in myrcene (Cavalo 57.1%, rose 52.4%, Sword 37.2% and Paulista 30.3%), and besides, this myrcene, mixed with other molecules of the same fruit, decreases their assimilation. Also, if the mango is not very ripe the myrcene level will be too low to notice its interaction.
Essential oil of hops can also be used (hydro-distillation of the unfertilized female flower). It contains more than 20% myrcene which can be assimilated very quickly.
Terpenes open the door to numerous scientific researches and investigations, particularly on a medical level. For example, if we add more limonenes, we will have a more stimulating herb, and on the contrary, if we increase linelool levels of a plant, its effect will be much more sedative.
For more imformation visit the links below.

Entourage Effect ? Cannabinoids & Terpenes
Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid-terpenoid entourage effects
Marijuana and the Cannabinoids Forensic Science and Medicine
Aroma Volatile Constituents of Brazilian Varieties of Mango Fruit
Halent Laboratories