Deficiency and excess of Potassium in cannabis plants
List of contents
In the complex cocktail of essential elements for correct plant development, potassium stands out as a vital director that orchestrates numerous fundamental processes in plant cultivation. In today's article, we are going to see the main characteristics of potassium, exploring its crucial role in strengthening cellular structures, regulating water balance, and enhancing resistance to environmental factors.
In addition, we will also see the main symptoms of a deficiency or excess of this element, known for its impact on the health and vigor of plants, and which plays a transcendental role in numerous plant vital processes.

The Potassium Cycle
Potassium is an element that we find on Earth in the form of a mineral. This mineral is more or less present depending on the type of land in which we grow. Soils composed of clay are by far the richest in potassium, which can contain up to 3%.
Through rain, aquifers, and rivers, this element goes to the oceans and seas where, by evaporation, it returns to the sky in the form of water vapor to pass again in the form of precipitation to the mother earth.
One of the ways that this element self-regenerates on Earth is through animal excrement. Potassium returns to dry land to be processed again by soil microbial life. The remains not used by the plants that have been washed away by the rain return through the aquifers to the sea and oceans to be returned to the earth again and close the potassium cycle.
In those regions where rainfall is constant, the substrate will not have good retention of this nutrient, and consequently, it will not be found in the substrate in the quantities that the plants demand. It is a very easy element to drag with large amounts of water. Thus, we must add potassium in the form of sulfate to add this element back to the substrate and make it available to the plants.
Products to enhance microbial soil life
Feeding the soil is crucial to achieve best results when growing organic cannabis. In this article we tell you how to do it and what are the best products to enhance the microbial soil life, which highly improves nutrient uptake and has a direct impact on the overall performance of your plants.
Functions of potassium in marijuana
Potassium is one of the most important nutritional elements for marijuana plants, present in all types of fertilizers and additives, such as PK boosters. Although they are not so present in plant tissues, they do perform important functions as a catalyst for many metabolic processes such as those we can see below:
- It intervenes in photosynthesis, promoting the synthesis of carbohydrates.
- It intervenes in synthesizing proteins and amino acids which come from nitrogen in the form of ammonium, so the interaction between the two nutrients is vital to carry out the different metabolic processes of plants.
- Increases the plant's resistance in periods of drought.
- Increases the consistency and hardness of plant tissues.
- Together with phosphorus, it increases the hardness and resistance of the root system.
- Frost resistance increases by acting as an antifreeze, acting within the plant sap.
- Increases the weight, density, and volume of the flowers.
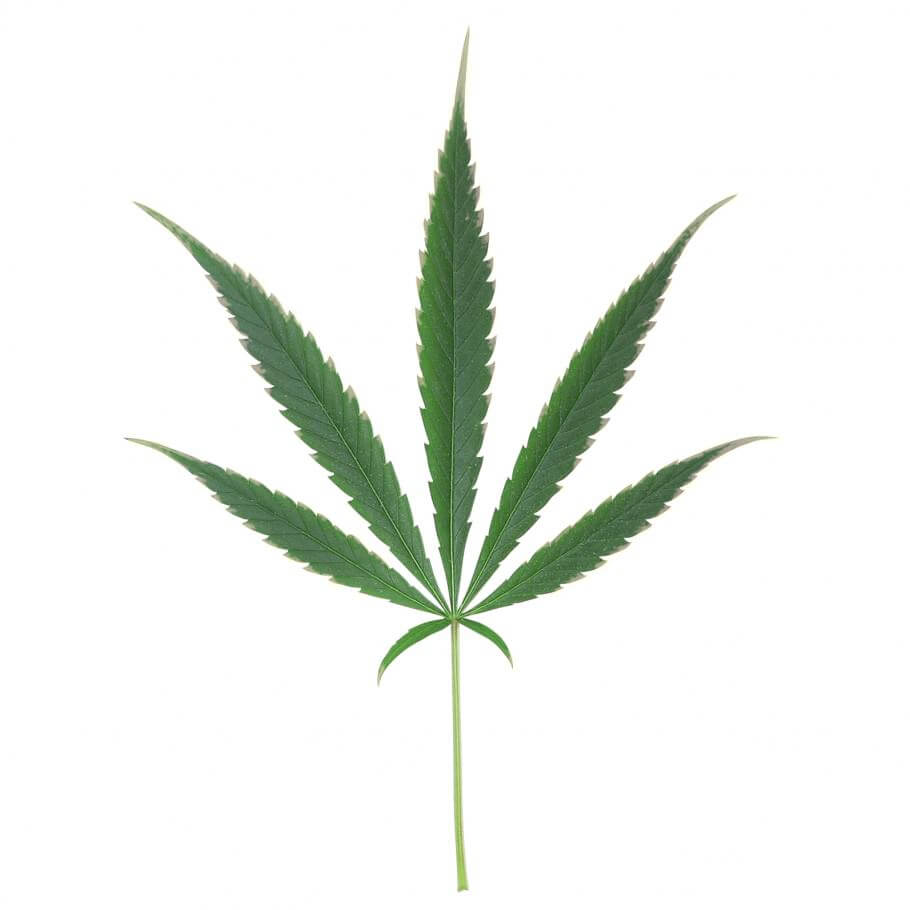

Potassium deficiency in marijuana plants
In the case of a Potassium deficiency, the plants will have visible symptoms that will help us detect said deficiency. This is a mobile element so that when the plant needs it, it will move from the oldest leaves to the youngest, always being the part of the plant with the most activity in its metabolism. We must ensure that this nutrient is not lacking in crops since a visible and advanced potassium deficiency means that the plant's production will already have been reduced.
In the case of potassium deficiencies, we must add more nitrogen fertilizer, whether of biological or mineral origin. Organic fertilizer is slower to absorb than mineral fertilizer, which in a short time will have been able to solve this deficiency and be able to harvest some decent buds. If the deficiency is premature we can simply increase the dose of fertilizer in organic or mineral format according to the preferences of each grower.

Symptoms of potassium deficiency:
- The tips of the plants turn yellow and this spreads towards the center, ending at the base of the leaf.
- The plants have no vigor and have little resistance to diseases.
- The stems are weak and bend easily.
- The final production of buds is seriously reduced.
- An excess of calcium can reduce the plant's ability to absorb potassium, creating a deficiency.
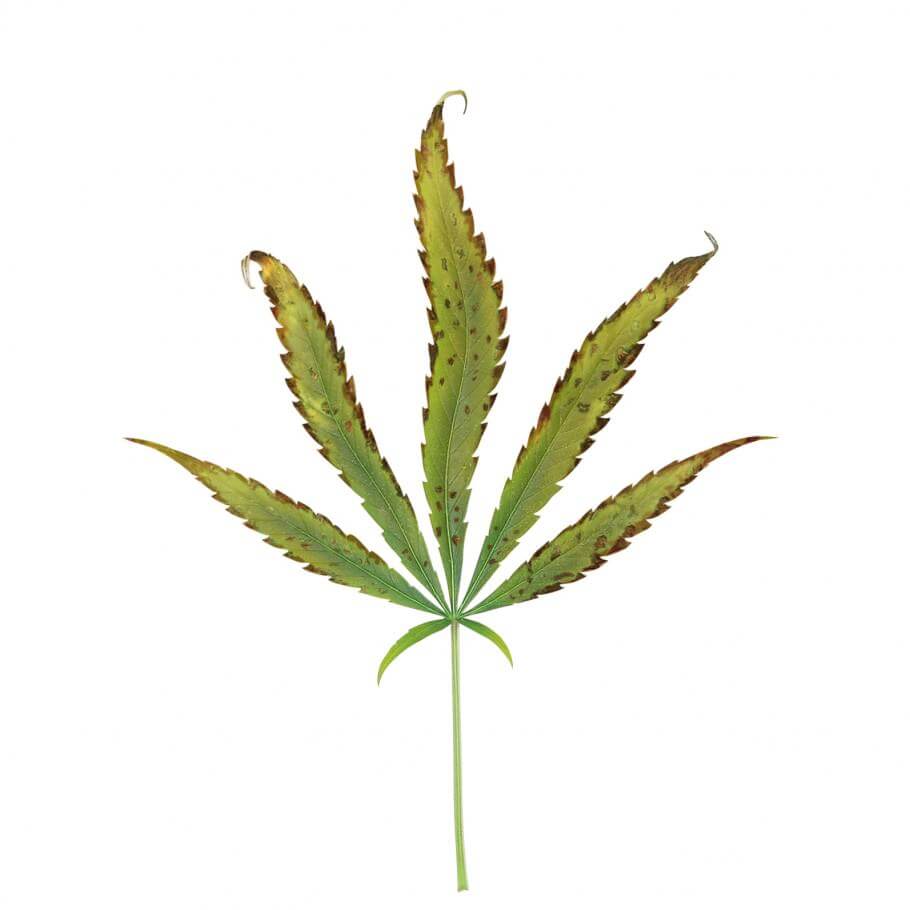

Excess potassium
Excess potassium in plants can manifest itself through various symptoms. Here are some common signs of too much potassium.
Symptoms of excess potassium:
- Marginal chlorosis: Leaves may develop chlorosis, a generalized yellowing, with a dark green edge.
- Leaf necrosis: Brown spots or necrotic areas may appear on the leaves, especially on the edges.
- Decreased absorption of other nutrients: Excess potassium can interfere with the absorption of other essential nutrients, such as magnesium, zinc, iron and calcium, leading to deficiencies of these elements.
- Reduced growth: Although potassium is necessary for plant growth, too much can inhibit the absorption of other nutrients and negatively affect overall growth.
- Reduced cold tolerance: Plants with excess potassium may become more susceptible to cold damage.
- Nutritional imbalances: An excess of potassium can cause nutritional imbalances since it can displace other cations in the plant's absorption.
Please note that symptoms may vary depending on the variety and specific growing conditions. Carefully monitoring plant health and adjusting fertilization rates as needed is key to preventing problems associated with excess potassium.
To treat an excess of this element, a root wash must be carried out with a minimum of three times the water capacity of the pot, aided by enzymes, which will act as a salt breaker. Subsequently, we must water with a light, complete, and balanced fertilizer, always adjusting the pH according to the phase in which the plant is.
Happy harvest!