Deficiency and excess of Phosphorus in Cannabis plants
List of contents
In the field of agriculture, phosphorus emerges as an essential element that triggers a series of fundamental processes for the correct flowering of plants. From the development of extensive and effective root systems to the activation of vital metabolic processes, in this article, we invite you to explore the importance of phosphorus for your plants.
Discover how this element, present in most flowering fertilizers but also many root stimulators, plays an important role in both the growth and flowering phases of plants, and how its strategic management can mark the difference in the quality and yield of crops.

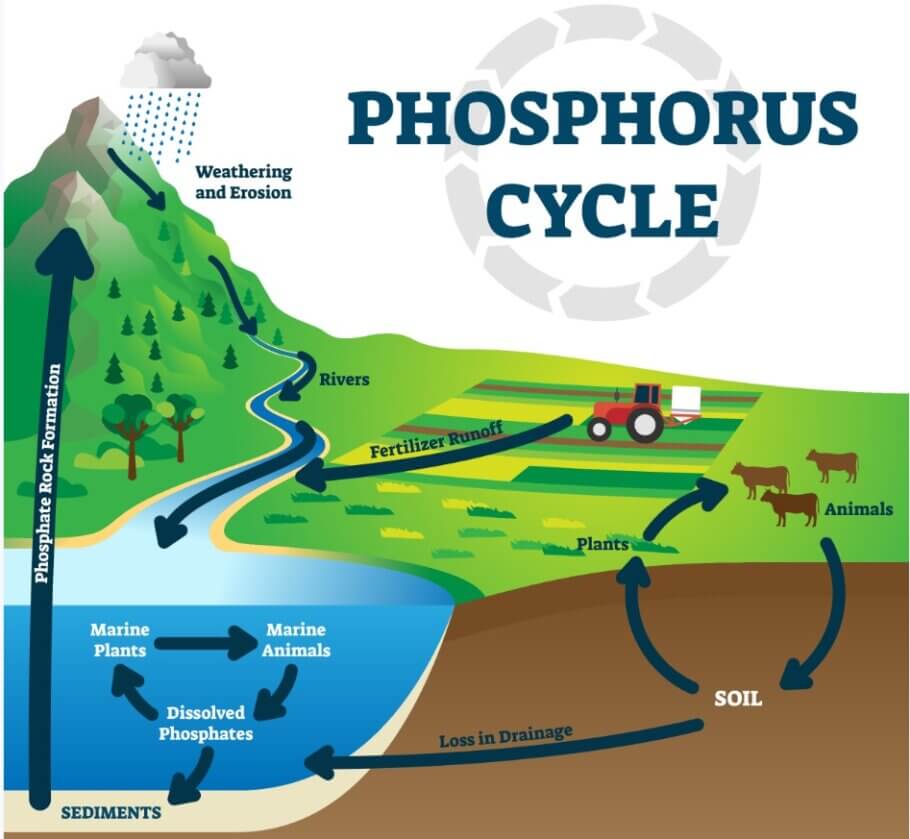
The phosphorus cycle
In the same way as with other elements, before we can use phosphorus as fertilizer we must wait for Mother Nature to carry out a series of processes to be able to use it as a raw material. Phosphorus is an element defined as a macronutrient since it intervenes directly and in large quantities in the metabolism of all plants, and especially in cannabis.
The phosphorus cycle is known as the biogeochemical cycle and always occurs in an ecosystem within a closed cycle that is constantly repeated on our planet. It is living beings that feed on phosphorus, either through phosphate decomposition processes or through already phosphate rocks.
These phosphates come into contact with plants through the soil. The animals feed on these vegetables, which contain quantities of phosphorus that will be contributed again in the form of excrement to the subsoil, to later be treated by microbial life, adapting the phosphorus again in the form of phosphates, which can be absorbed again by of the plants, thus closing the phosphorus cycle.
On the other hand, a large part of these phosphates present in the substrate are dragged into the sea, so that all marine fauna and flora are impregnated with this mineral. Phosphorus returns to the terrestrial environment through two systems; the first, is through the excrement of seabirds and fish, which have previously fed on the algae from which they have also absorbed phosphorus into their organisms. The second method is from earth movements that emerge outside, that is, tectonic plate movements, although this process lasts thousands of years.
Functions of Phosphorus in marijuana plants
Phosphorus is an essential nutritional element for cannabis plants. It is known that much of the energy that the plant receives from sunlight is later stored, much of it in the form of phosphorus. Subsequently, it is used to carry out different metabolic processes such as photosynthesis, being in turn a component of DNA.
We can say that this macronutrient is very important for the development of plants in their different stages of life, whether we are talking about germination, root growth, growth of the aerial part, cloning, or flowering.
Plants absorb phosphorus in the form of monovalent and bivalent ions, although the most used by the plant is the monovalent ion, which will be more or less available depending on the pH range of the substrate. The higher the pH, the less the plant will absorb this nutrient, causing it to show signs of deficiency.
How to increase the THC level of cannabis plants
Getting the maximum performance from plants is the main objective of every grower, whether we are talking about flower production or cannabinoids and terpenes. Especially in recent years, with the rise in the therapeutic use of THC, getting genetics with a high content of this cannabinoid has become the goal of many breeders, while getting the most out of them is the goal of many growers. Today we are going to tell you some tricks to get the THC content of your flowers even higher, of course within the limits set by the genetics themselves.
From the absorption of this macronutrient, plants can carry out different biochemical actions such as respiration, in addition to synthesizing proteins along with carbohydrates. Its functions translate into:
- Greater root development
- Better use of substrate water
- Stimulation of the general vigor of the marijuana plant
- Formation of more robust stems
- Greater resistance to frost, insect attacks, and diseases
- The duration of the vegetative period is significantly reduced given the vegetative explosion produced by rapid root growth. You can switch to the flowering period early and, consequently, the total time needed to grow cannabis will be reduced.
- Increase in production and improvement in the quality of buds and seeds
- Direct influence on the production of carbohydrates, improving the production of sugars and starches, producing better quality fruits
Phosphorus deficiency in marijuana plants
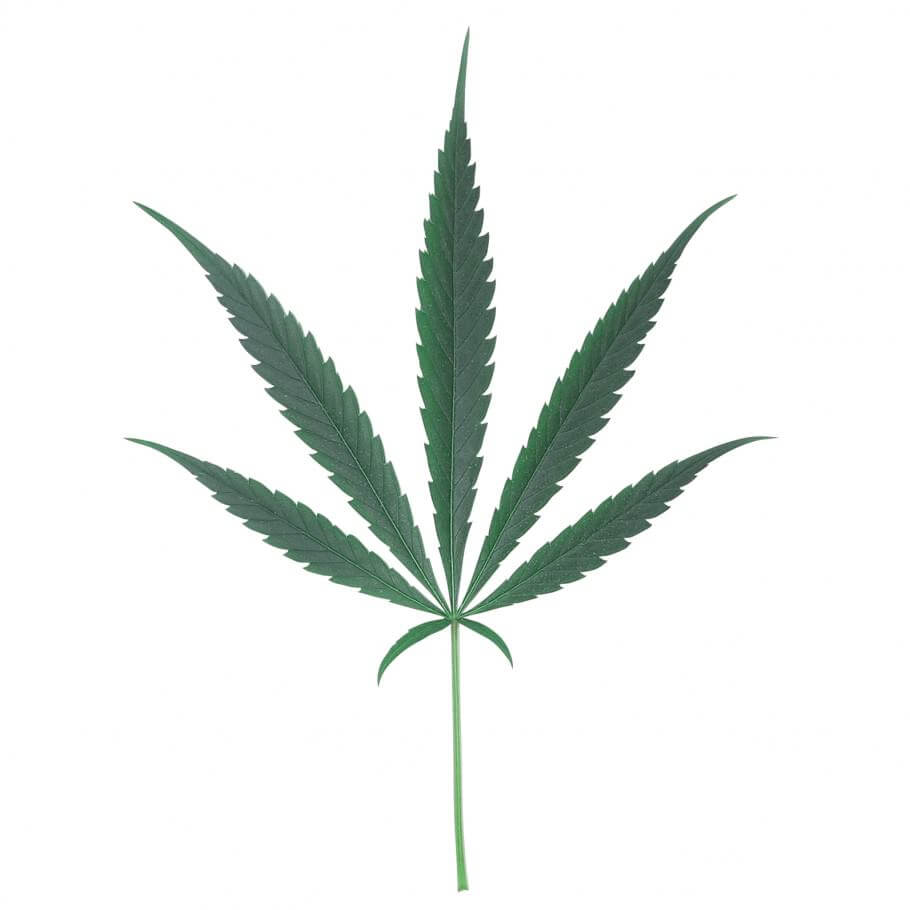

Poor assimilation of phosphorus - or the absence of it - will result in a deficiency of this element. Like nitrogen, this nutrient is mobile, which means that it moves easily within the plant's body, moving to those areas with the most activity, such as the youngest leaves.
When this element moves from the oldest leaves to the youngest, the former suffer chlorosis, turning yellow. The oldest and lowest leaves of the plant act as a reserve of nutrients that the plant will use when required.
As the deficiency develops, chlorosis will advance through the plant, affecting all the leaves, and turning yellow. If it is not remedied, the plant will suffer massive defoliation, leaving it without leaves to be able to carry out its vital functions and facing premature death.
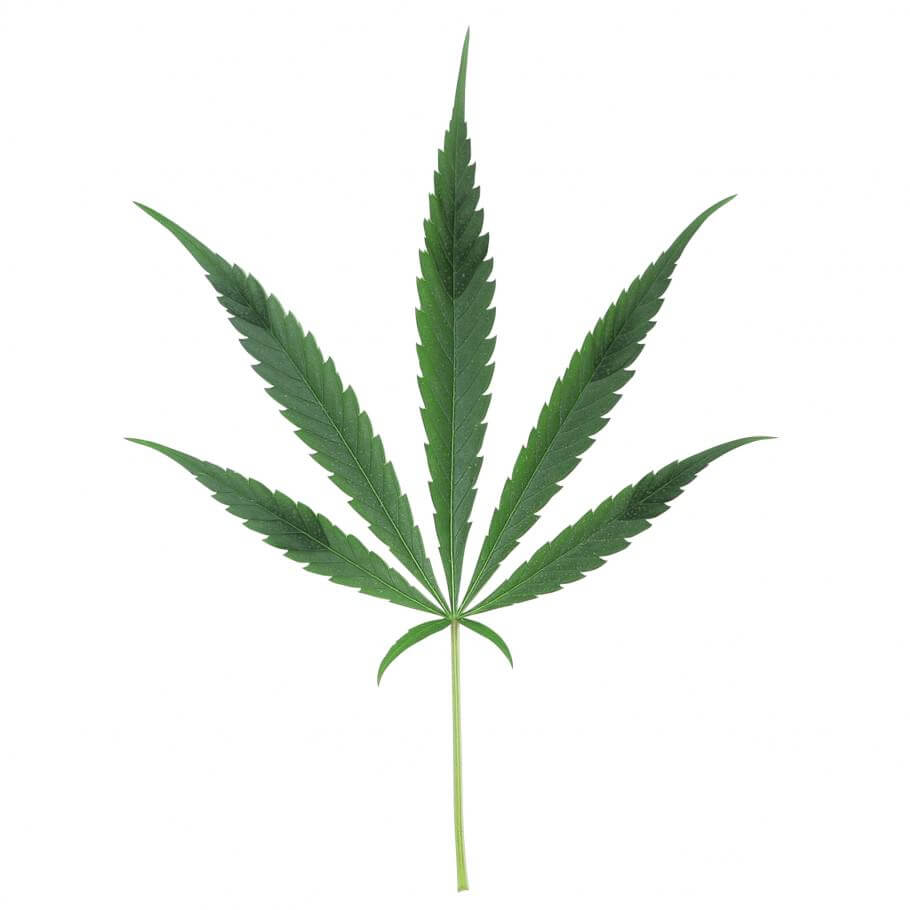

The lack of this element affects the plant in the following way:
- Delayed growth of smaller leaves.
- The stems, petioles, and other parts of the plant change to a purple hue.
- The tips of the older leaves are claw-shaped along with dark green-blue colors.
- The most affected leaves create necrosis, acquire a purple/tan color, dry and wrinkle, and finally fall off the plant.
- The buds are smaller and do not develop as they should.
- Plants are more vulnerable to any type of infection whether caused by diseases, fungi, or insects.
How to treat phosphorus deficiency
- We must regulate the pH of the substrate between 5.5 and 6.5 depending on the type of substrate used; In hydroponics, the range will differ between 5.5 and 6.2 depending on the cultivation phase.
- With excesses of other elements such as zinc or iron, phosphorus will be blocked. To correct the blockage we must carry out a root wash with a stable pH according to the growing phase and then carry out a light irrigation with a balanced fertilizer rich in phosphorus.
- The fertilizers to use to solve the deficiency can be organic or mineral in nature, the mineral being the most quickly absorbed by the plant.
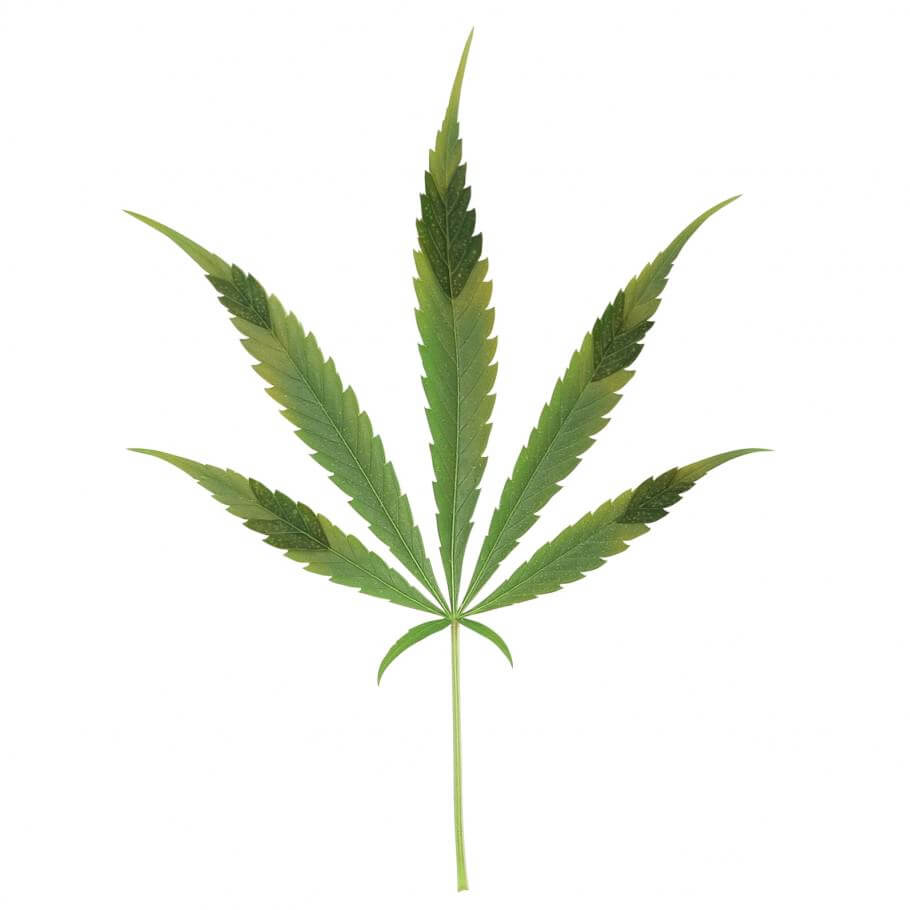

Excess Phosphorus
Excess phosphorus affects the plant by blocking many other nutritional elements such as calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, and zinc, with zinc being the easiest microelement to block. In this way, you should be attentive to deficiencies in other elements to know the severity of the excess of Phosphorus.
If there is an excess of this element, wash the roots with a minimum of 3 times the capacity of the pot. The washing water can be composed of a mixture of water with enzymes (which act as salt breakers) to facilitate cleaning, with a stable pH value depending on the life stage of the plant to be treated.
These are some of the symptoms of excess phosphorus :
- Dark or purple coloration: Leaves may show dark or purple coloration, especially on the edges.
- Delayed growth: Plant growth may be slowed, and new leaves may be smaller than normal.
- Zinc Deficiency: Excess phosphorus can interfere with zinc absorption, which can result in zinc deficiency symptoms, such as yellowing between the veins of leaves.
- Chlorosis: Leaves may experience chlorosis, which manifests as generalized yellowing, although the veins remain greener.
- Problems with mycorrhizae: An excess of phosphorus can interfere with the formation of mycorrhizae, and symbiotic associations between plant roots and beneficial fungi. This can negatively affect nutrient absorption.
- Phosphorus Accumulation in the Soil: In soils with excess phosphorus, plants can show symptoms of toxicity, even if they are supplied with a normal amount of the element.
It is important to keep in mind that these symptoms can vary depending on the variety you grow and, of course, the conditions in which your plants are found. Careful observation and monitoring of plant health are essential to determine the presence of excess phosphorus and adjust fertilization practices accordingly.
Happy harvest!