Growing marijuana in plant pots
List of contents
- Which type of soil should we use for growing marijuana plants?
- How to enrich the soil before its use?
- How to make good use of the microbial life in the soil?
- What type of fertiliser should be used for growing marijuana plants in soil?
- Is it necessary to correct the PH value in soil marijuana crops?
- What type of containers should be used for growing marijuana plants in soil?
- How to transplant your marijuana plants?
- Is it possible to use the same soil several times?
- What are the advantages of growing in soil?
Growing marijuana in soil is, by far, the most common type of crop throughout the world. In this post, we are interested in how to optimize our soil in a simple and fast way.
Which type of soil should we use for growing marijuana plants?

We recommend you to use, whenever possible, a soil specially developed for marijuana plants, which will offer much better results than any classic gardening substrate.
In fact, using a soil specially developed for the cultivation of cannabis will be an easy way to optimize the crop regarding both the structure (drainage, aeration ...), PH, and nutrients (fertiliser) contained. Canna Bioterra, for example, provides excellent results.
How to enrich the soil before its use?
There are several organic fertilisers to enrich the soil before its use. This will allow you to reduce the amount of liquid fertiliser used in the crop; actually, not using any fertiliser is possible if you use large containers.
For example, you can do the following mixture:
- 100L of soil for marijuana plants
- 10-20L of Vermicompost (Humus), a natural complete and very balanced fertiliser.
- 2-5L of Bio Super Mix, a mixture of organic fertilisers from Plagron, which has many nutrients, trace elements and beneficial microbial life.
- 1 kg of bat guano, a source of phosphorus (P) and elicitors which will enhance the natural defenses of the plant (resin)
- 1 kg of wood ash (barbecue, fireplace, etc.) source of Potassium (K) and coal for the microbial life.
- 200 gr. of Nutrihemp, a natural fertiliser based on algae, source of Nitrogen (N) and amino acids.
These are slow release fertilisers, what means that they will degrade gradually in the soil over the course of several weeks. Thus, the risk of over-fertilization is low, in contrast to liquid fertilisers which are assimilated much faster.
You can also improve the structure of the soil by adding:
- Coconut fibre (20%) and/or Perlite (10%), to increase the drainage capacity and aeration of the soil.
- Polymers, to ensure a small reserve of water and thus reduce the frequency of watering.
Clay Pebbles on the bottom of the pots aren?t useful, even if this technique is very frequently used. They reduce the amount of available soil and raise the PH if they aren?t correctly prepared a few weeks before.
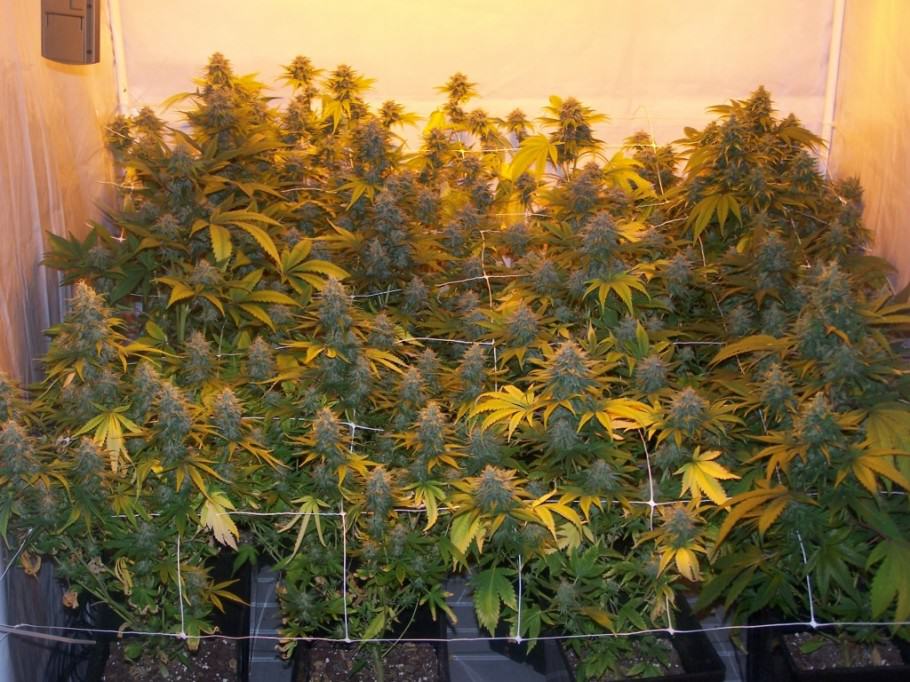

How to make good use of the microbial life in the soil?

One of the most significant advantages of growing marijuana in soil is using the active beneficial microbial life of the soil (bacteria and fungi) in natural symbiosis, which perform two important actions:
- Break down large organic molecules and dead roots into easy-to-assimilate nutrients for the plants.
- Protect the roots from attacks of harmful bacteria or pathogenic fungi (vectors or triggers of diseases)
The microbial life of the soil goes unnoticed by large part of the marijuana plant growers, while this directly influences in the development of the plant, increasing the quality and quantity of the yield.
You can add some strains of carefully chosen bacteria or fungi in order to significantly improve the quality of the microbial life of the soil. These bacteria will act in symbiosis with the roots of the plants: microbial life will receive the needed sugars for its development through the nutrients provided by the waterings.
The most well-known and probably the most efficient one is called Trichoderma Harzianum, from the family of the Mycorrhizae. We can find it in products like Micoplant (microscopic fungi). BioMagix from GHE is a mixture of Trichoderma and beneficial bacteria. You can also add numerous fungi and favourable bacteria using Bactoforce from House&Garden or bacteria from Bactohemp.
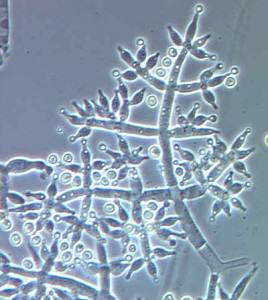
Once this microbial life is introduced and active, it will be necessary to have caution: do not use any bactericidal or fungicidal product that could get in contact with the ground: H2O2, Silicon, Propolix, Sulfur ?
Note that letting the tap water used to water our plants to rest for a few hours is also very important. This removes the chlorine through evaporation, since this is added in a gaseous form to the tap water to eliminate all bacteria and fungi contained in it.
Beneficial microbial life creates its own enzymes to break down organic molecules, so it isn?t necessary to add them in liquid form. Enzymes have been developed to replace and simulate microbial life when not present (hydroponics etc.).
If you want to sterilize the soil to eliminate all bacteria, fungi, eggs, larvae, insects, mites, etc, you only have to put it for some seconds in the microwave. Don?t forget to add new microbial life once the soil is sterilized.
Sugars (molasses, glucose ... ) will greatly increase the microbial activity, as well as the humic and fulvic acids, such as those contained in Diamond Black from General Organics.
What type of fertiliser should be used for growing marijuana plants in soil?
In order to properly help the microbial life, it will be very important to use organic fertilisers (bio) specially designed for marijuana plants, such as:
- Bio Vega and Bio Flores from BioCanna
- Bio Thrive Grow and Bio Thrive Bloom from General Organics fertilisers
- Bio Grow and Bio Bloom from Biobizz
Of course, it?s also possible to grow in the ground with mineral fertilizers (chemicals), these are directly assimilated by the plant without passing through the microbial life. This micro-life, then, doesn't have many elements for its nourishing; its development will not be so pronounced than when using organic fertilisers.
This is the biggest difference between organic and mineral fertilisers; the former feed the soil and the plant at the same time, leaving a rich and alive substrate, while chemical fertilisers only feed the plants, leaving a poor and barren substrate. Leaving aside marijuana plants, this problem affects all soil crops around the world.

Organic fertilisers, when properly used, allow yield as high as mineral fertilisers. However, it's especially to achieve the best quality in taste that using organic fertilisers is advisable (bio), what provides the crop with richer and more complex flavours than mineral nutrients.
To avoid accumulations of salt or chemicals in the soil, it will be necessary to water without fertiliser intermittently, doing one watering with fertiliser and another without it, or up to two irrigations with fertiliser for only one with water.
Above all, remember that the final flushing of the roots should be performed only with water - without fertilisers - at least 3 weeks before the harvest to be efficient (the longer the root washing period and the cleaner the roots are from nutrients, the better will be the quality of the taste).
Don?t hesitate to read our post about watering marijuana plants in soil.
Is it necessary to correct the PH value in soil marijuana crops?
When using organic fertilisers - and with a PH level from 5 to 8 - it won?t be necessary to correct the PH level. The soil itself has good buffers to regulate the PH, which are responsible of softening pH fluctuations. The ideal PH level for growing in soil is about 6.5.
If you use acids to reduce the PH level, this will destroy this buffer effect, so adjusting the PH in each watering during the entire crop will be necessary.
In practice, a PH value near 6.5 is advisable only when:
- Using mineral fertilisers to improve nutrient uptake.
- Using water with a PH range lower than 5 or higher than 8.
- Growing mother plants, because the natural buffer of the soil is reduced over time.
To lower the PH level in organic crops (bio) we can use citric acid or lemon juice.
Measuring the EC value (Electrical Conductivity) won?t be entirely necessary with organic fertilisers, because the EC meter won?t provide exact measurements of real nutrient concentrations in the soil. Although it should be noted that we can control the specific amount of mineral fertiliser used during a crop and for a particular marijuana strain to have different benchmarks for future crops with the same genetics.
What type of containers should be used for growing marijuana plants in soil?
The roots usually tend to mainly colonize the external part of the pot, so changing to a larger pot during the cultivation is very useful. It will create a much more efficient root system, what will make the watering and nutrition of the plants much easier. The pots should always have holes in the bottom to ensure effective drainage in case of excessive watering.

Outdoors, a large pot will ensure great yields, this is why growers normally use 30-50L (or larger) containers during the bloom phase. In the case of regular marijuana seeds you can wait until the beginning of the flowering phase to transplant the plants, when we know if they?re males or females.
Autoflowering marijuana strains don?t follow these rules due to their small size and short growth period. Growing this type of plants directly in the final pot (10-20L) is recommended to achieve best results with automatic strains. (Big Devil XL, Think Different, Flash Seeds?)

It?s not advisable to grow several plants per pot, because both both branches and roots will compete for the available space. If you want to do it, use large containers (growing trays) and leave the longest possible distance between plants.
Plastic pots weigh less and consume less space than clay pots, so they are more comfortable to use. Square pots are more efficient than round ones. Finally, white pots are better to protect the roots from the summer heat.
The oxygenation of the root system is, unfortunately and too often, the limiting factor when growing in soil, so we should avoid pressing the soil. We should also scratch the surface of the substrate before watering for a better absorption of the irrigation water.
To improve the oxygenation of the roots in the ground we can use smart pots, which allow maximum aeration of the substrate.
How to transplant your marijuana plants?

During the transplant we must avoid to stress the plant, particularly in the root area.
Transplanting is much easier when the ground is relatively dry, so doing it between irrigations is advisable.
Make the transplant as follows, from a small pot (A) to a larger container (B):
Put some soil on the bottom of the larger pot (B), and place the small pot (A) in the center, add soil on the sides and until filling the pot. Press gently the soil (B) and then remove the smaller pot (A).
In this way, we have a hole of the size of the smaller pot (A) in our larger container (B). Remove the plant from its pot and place the rootball in the hole (B).
Add a some soil on the surface to completely fill up the pot (B). Water the plants with root stimulator (this product contains vitamins that reduce the stress caused by the transplant) but without fertiliser (the new soil contains all the necessary nutrients for some days/weeks)
Is it possible to use the same soil several times?
We recommend you not to use the same soil for several crops, since its internal structure is degraded over time (Oxygenation, drainage, buffers ... ) and it contains residues of fertilisers or products from previous crops.
However, you can always use it again in your garden or for other home plants (Ficus, etc).
What are the advantages of growing in soil?

First of all, growing cannabis in soil allows us to use organic fertilisers in combination with beneficial microbial life, achieving great results with top grade flavours.
The second great advantage is its relative tolerance to mistakes, thanks to its powerful buffer effect. For this reason, it?s recommended for novice growers who begin growing marijuana plants, because in this way they can learn the basics of cannabis farming without the need to use expensive hydroponic systems, which are also more difficult to control.
Soil will remain for a long time as the most commonly used substrate for growing marijuana plants, and let us hope that this easy and natural growing method will allow you to get the best from your plants !