Deficiencies and excesses of nitrogen
List of contents
In the world of agriculture and plant growing, nitrogen is an essential element that plays an important role in the development and health of plants. Today we invite you to discover the complexities and benefits of nitrogen in the growing process, the different types of nitrogen that can be found in fertilizers, its impact on plant growth, and other fundamental aspects that make it an essential element for crop success.
Without a doubt, nitrogen is one of the most important elements in cannabis cultivation, which promotes healthy and vigorous growth and which, of course, cannot be missing from any balanced diet for plants. We tell you everything below!

Nitrogen (N) in cannabis cultivation
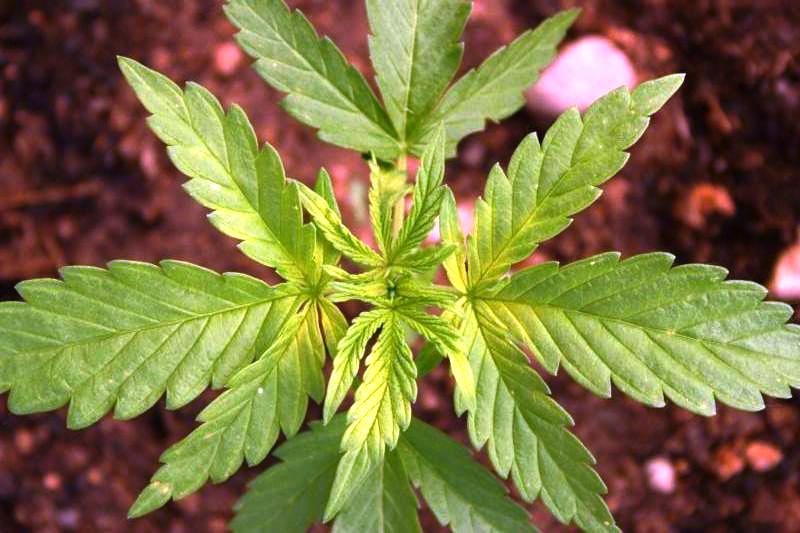
Nitrogen as a nutrient is a very important mobile element that interacts directly in the development of marijuana plants during all their life phases. Depending on the life stage of the plants, they will have a greater or lesser demand for this nutrient.
Nitrogen regulates the capacity of marijuana plants to create proteins, amino acids, enzymes, chlorophyll, alkaloids, and nucleic acids, being mainly responsible for the growth of the stem, leaves, branches, and vigor in general.
Nitrogen can be found in different formats: organic, ammoniacal, and nitric. The basic difference between these formats is the speed of nitrogen absorption by the plant, with the ammoniacal format being the one with the fastest absorption and consequently, the one that can more easily produce an excess of this nutrient.
On the contrary, nitrogen in the form of nitrate is also easily absorbed by the plant, although it does so more slowly. It is for this reason that in liquid fertilizer bottles, we will find nitrogen mixed in both formats to balance the absorption of nitrogen by plants without them suffering from an excess or lack of this macronutrient.
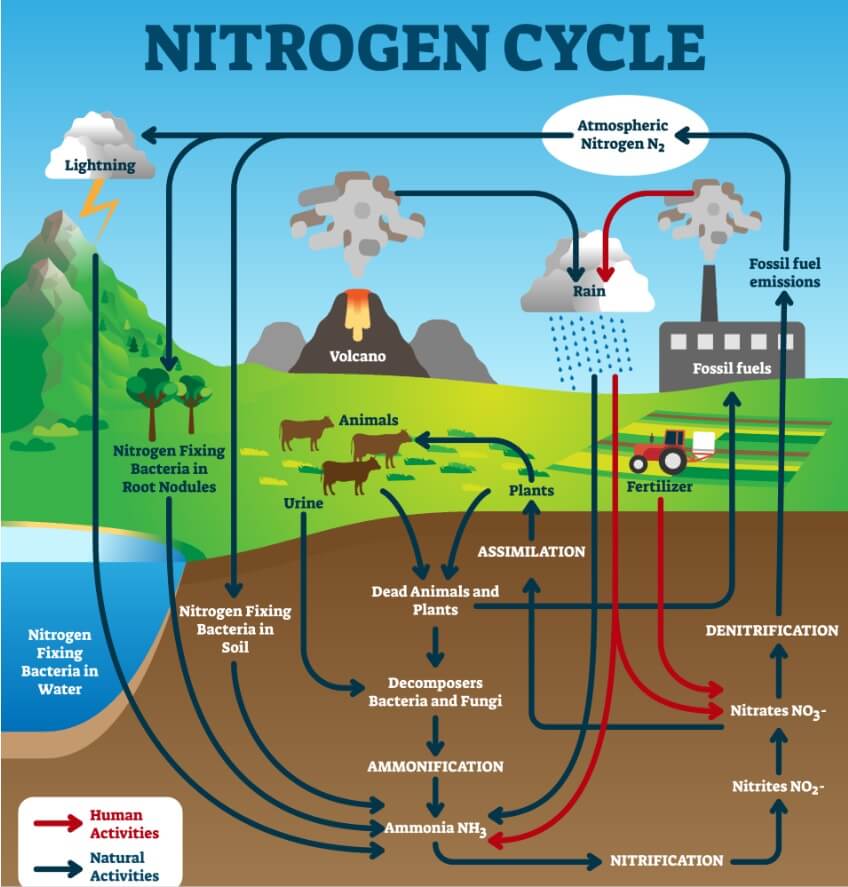
If the plants' demand is greater than the nitrogen they have at their disposal, they will suffer a deficiency; On the other hand, if the levels of this element are higher than what the plant needs, it will suffer from overfertilization.
We can find fertilizers in two formats such as mineral or organic. The mineral format has a faster absorption by plants since it does not have to be previously processed by the microbial life that lives in symbiosis with the soil to be absorbed by plants. Likewise, as we have already mentioned, you may find nitrogen-rich fertilizers in both liquid and solid formats.
An optimal level of nitrogen in plants will result in:
- Vegetative vigor
- Lush green color in the leaves due to the production of chlorophyll
- Increase in the number of plant leaves, stem span, fruits, and seeds
- Greater resistance of plants against fungi
- Greater resistance of plants against insects
- Greater resistance to frost and hail
Nitrogen deficiency in marijuana plants
When cannabis plants do not have balanced nutrition and a lack of this element occurs, abnormalities arise in their development that are visible through the morphology of the plant, which we call deficiencies.
- Plant growth is much slower.
- The leaves turn yellow gradually, starting at the bottom of the plant. Chlorosis begins at the tips and becomes lighter towards the center of the leaf.
- Plants have fewer defenses against pests, diseases, and stress.
- Flowering and seed production are seriously reduced.
- Massive defoliation after advanced chlorosis.
- The deficiency progresses from the bottom up, affecting the youngest leaves last.
To quickly solve the problem, a fertilizer rich in nitrogen in liquid form should be added to the nutrient solution so that the plants can recover their optimal levels of this nutrient a few days after watering.
It should be noted that when the plants already have these deficiencies, their capacity to produce will have already been reduced, so it is important to maintain a balanced diet throughout the crop to obtain optimal quality and production.

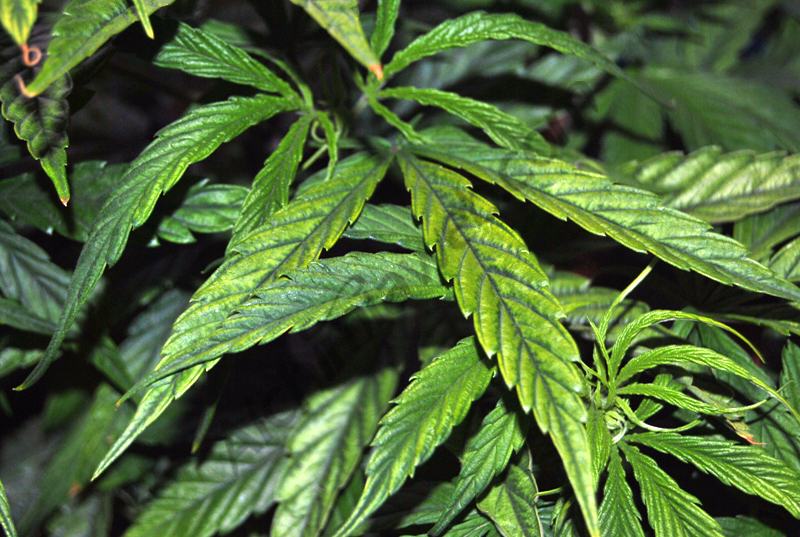
Excess Nitrogen in marijuana plants
On the contrary, excess nitrogen in marijuana plants also takes its toll by reducing their production and quality of flowers. These excesses can be recognized by observing the following symptoms:
- Excess foliage on the plant.
- Weak stems.
- Delay in the ripening of fruits, making them less sweet.
- Claw-shaped leaves facing the ground.
- Poor combustion of the buds
- Very intense green on the leaves
- Poor resistance to pests in general.
To solve this, we will carry out a root wash using three times as much water as the capacity of the pot along with low EC levels. We must measure the output EC to know how saturated the substrate is with salts and in extreme cases we will not stop washing until the nutrient levels of the substrate are the same as the water we use to wash.
For these processes, we can easily use salt-breaking products to help leach the substrate for faster recovery, like most enzymes.
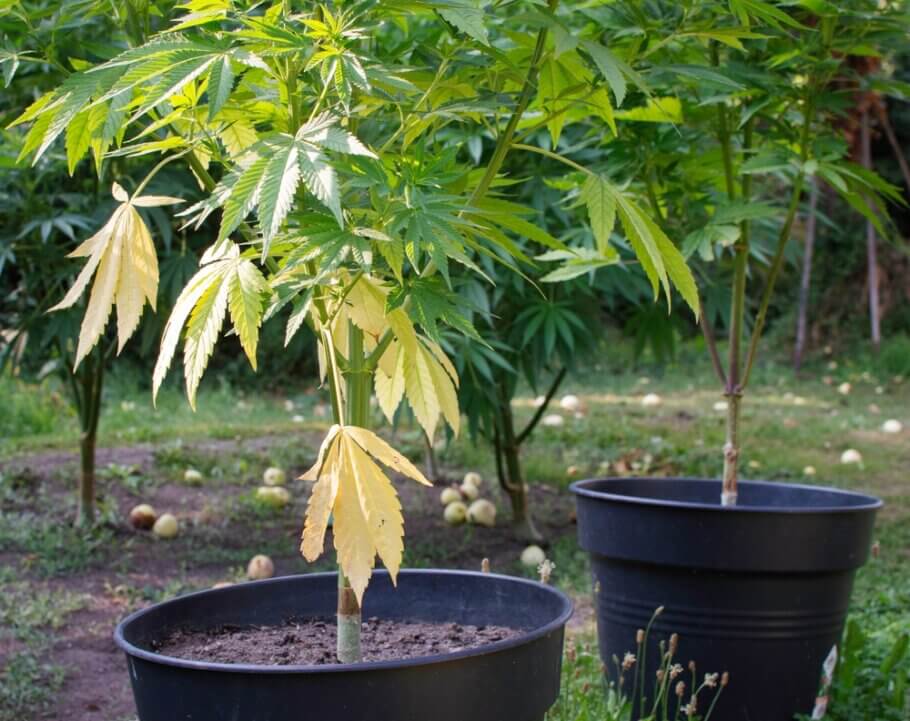

How cannabis recovers from excess nitrogen
Cannabis is a plant that, as we have already mentioned, is capable of morphologically showing its vital state so that it will be easy to know the state of our plants through its leaves, color, shape, etc.
In the case of having suffered slight overfertilization or in the opposite case in which there has been a lack of the same element, the cannabis plant will always take a few days to recover. The speed of recovery will always depend on the degree of deficiency or excess that the plant may have, so rapid detection will always help facilitate their recovery in a shorter time.
Depending on the substrate along with the fertilizers used, the plants may recover more or less quickly. In hydroponic growing systems, the speed of plant recovery will be much faster than in soil cultivation with organic fertilizers. As we have already mentioned at the beginning of the post, depending on the format in which the nutrients are presented, they will be faster or slower absorbed.
In the growth phase and in the case of a small overfertilization when there is an excess of this element, we will proceed to reduce or eliminate the growth fertilizer during a few waterings.
In the case of using additives for marijuana, we can continue adding them in the usual way since they do not contain food, only elements that will allow the plant to metabolize the excess food, creating more leaves, and branches ... in short, that grow and use up the nutrients they contain.

During the flowering phase, if we suffer from overfertilization we must act according to the crop week we are in. If it happens during the first two weeks after the change of photoperiod, we will act in the same way as if we were growing, since the plants will still grow almost until the 3rd week, when the buds begin to show.
On the contrary, if we are already in flowering, nitrogen excesses are not usually so common, but if there are then we must remove the base fertilizer, to continue fertilizing only with a PK supplement which does not contain added nitrogen. In this way, the plants can continue feeding to create buds depending on the phase they are in and at the same time eliminate excess nitrogen. In the case of more pronounced overfertilization, we can previously carry out a root wash to clean the substrate a little of excess nutrients and then irrigate with the appropriate doses of PK until indicated on the product label.
Happy harvest!