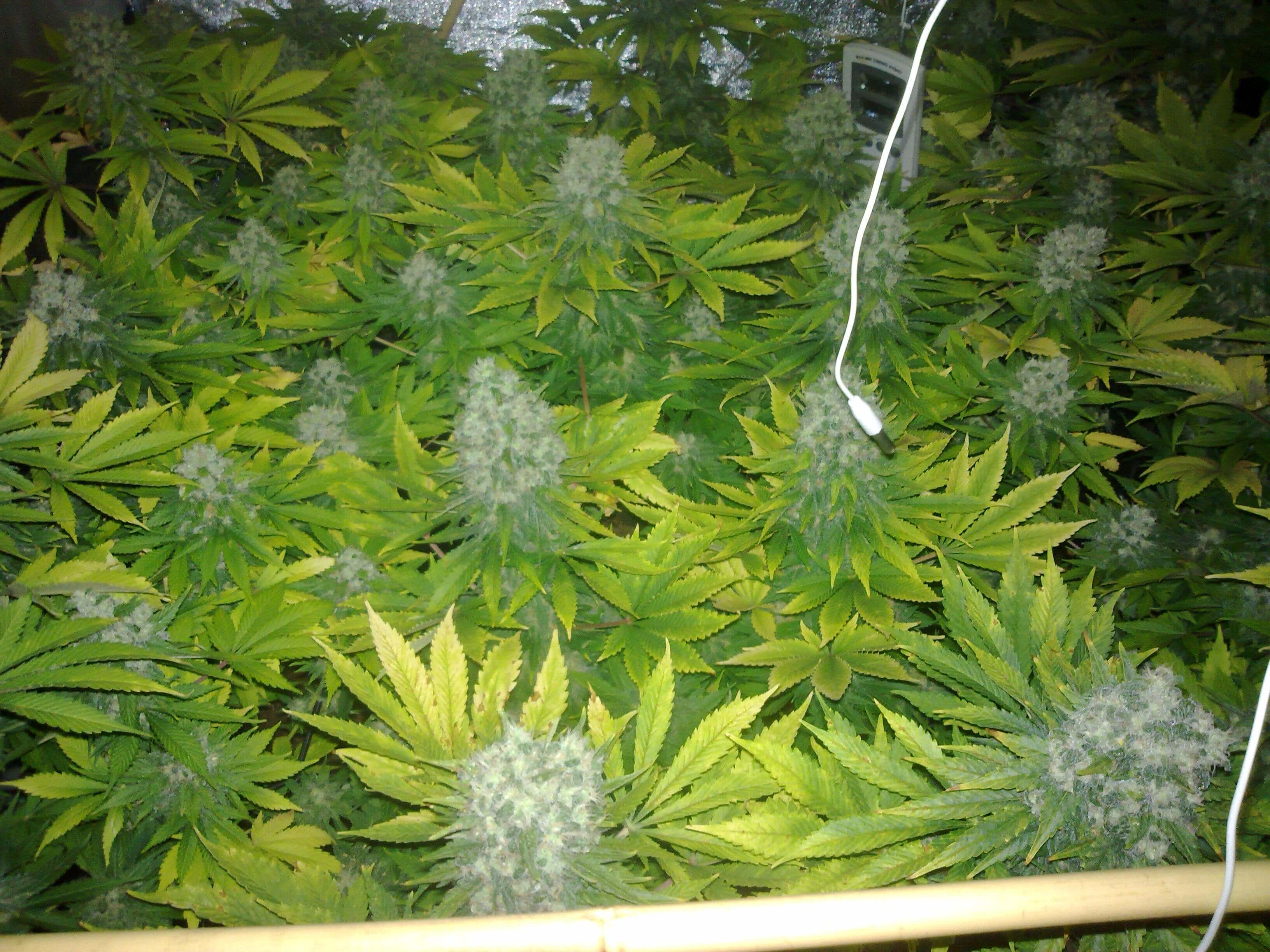
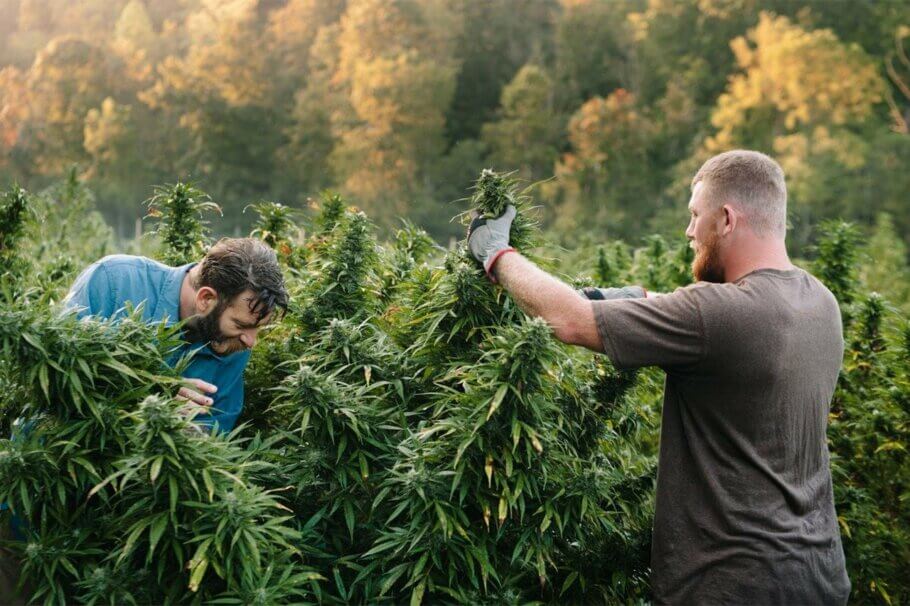
When growing cannabis indoors, the classic approach is to grow horizontally (or flatbed), generally using square or rectangular trays (depending on the shape and size of the grow tent or room), with the pots containing the plants placed side by side. Horizontally, one grow light is normally used to illuminate each square metre; and the plants are usually arranged in a “stadium shape” to take better advantage of the light: with the shortest plants placed in the centre and the highest around the sides.
However, every experienced grower knows that the maximum light output is still not always achieved and that many plants do not receive the amount of light they should. For this reason, vertical cultivation is an excellent tool for those who want to make the most of their resources indoors. Because vertical growth, when done correctly, can increase yields and maximise efficiency.
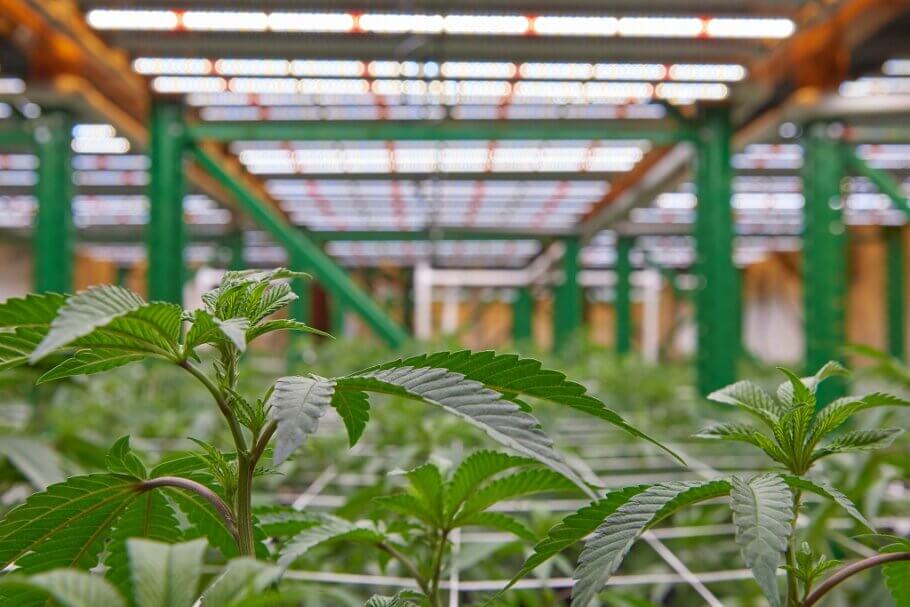
In many ways, it is a game-changer as the boundaries of innovation are being pushed upward. Vertical growing techniques provide opportunities that are unimaginable with traditional horizontal cultivation, particularly in more mature markets such as the USA, where commercial cannabis growers seek to improve yields, reduce costs and maximise space.
Vertical farming: less is more
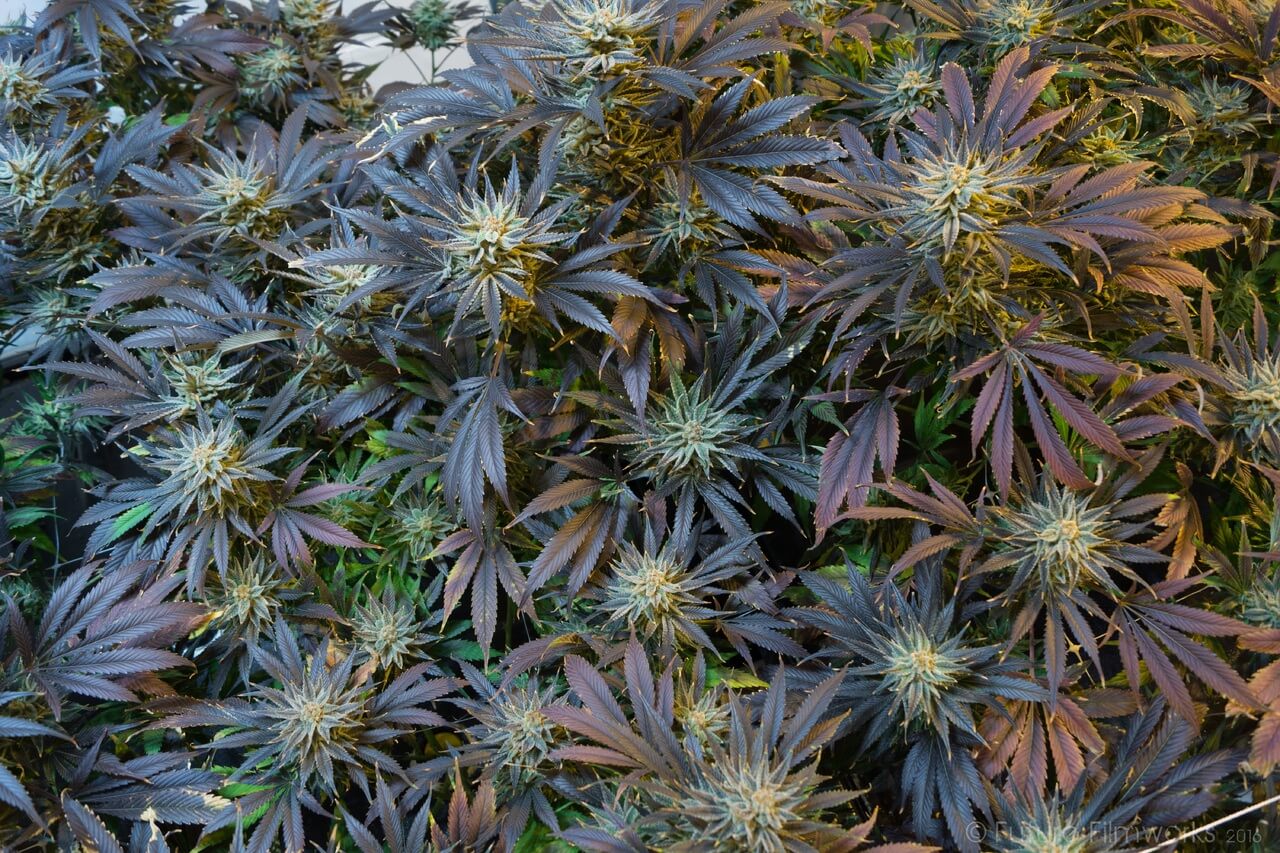
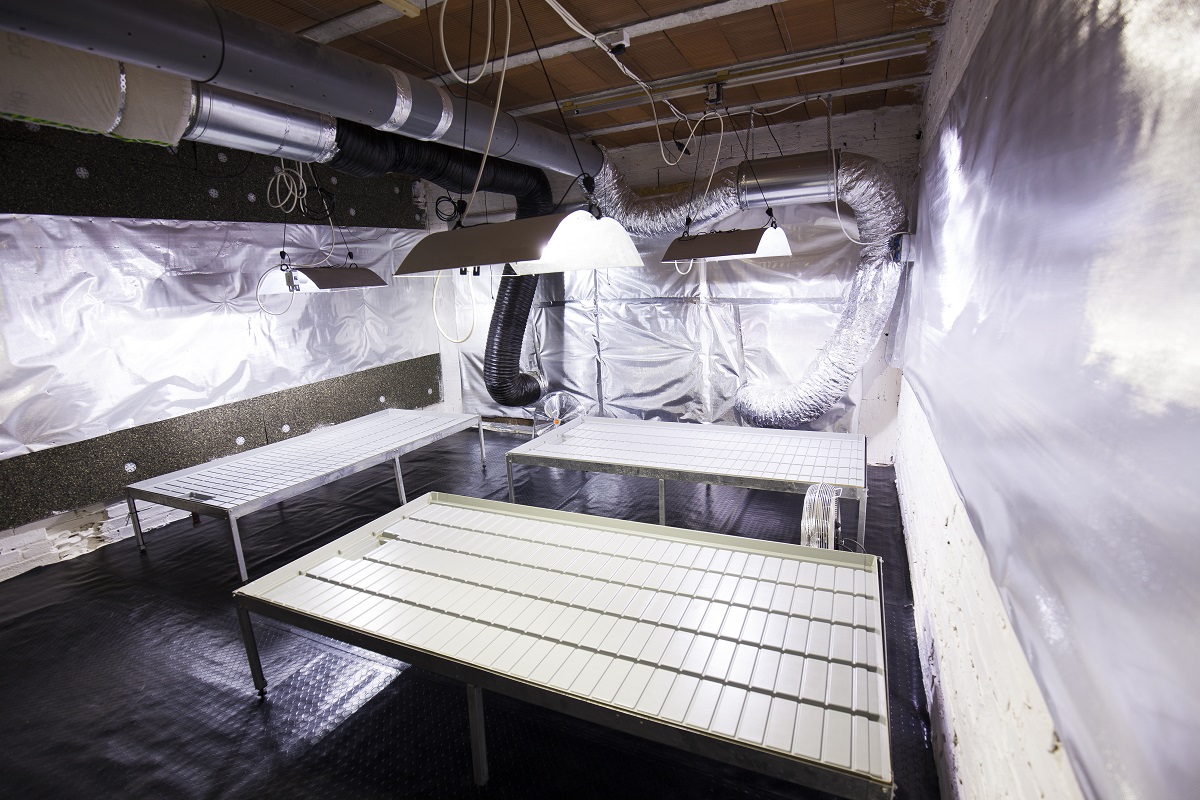
The vertical cultivation technique is the practice of growing plants in vertically stacked layers or sloping surfaces; It consists of placing the cannabis plants on shelves, walls, or in columns, with the light source placed in the centre or on each individual shelf layer. In this way, it is possible to take better advantage of the space and ensure that more light reaches all the plants, thus achieving a higher yield. It's all about maximising harvests while using the minimum available space.
Read more